Users want apps to be modern, intuitive, and easy to navigate, on both mobile and web. Meanwhile, developers are chasing something different: easy-to-maintain code that can be scaled while adding new features.
ReactJS is a strong front-end development JavaScript library that delivers a smooth experience on mobile and web. There are multiple frameworks aside from React, like Angular, Vue, Svelte, etc, for frontend development. But, according to the Stack Overflow survey, 45% wanted to use React. Furthermore, many users on Reddit concur that React continues to be a top choice for modern front-end development.
In this article, we will discuss why ReactJS is a preferred choice for front-end developers.
A Quick Overview of ReactJS
React.js is an open-source JavaScript library for creating user interfaces. It was developed by Jordan Walke at Facebook (now Meta) and was released in May 2013.
React leads front-end development with a modular structure. With that, developers don’t have to code the entire user interface in one block. Instead, they can use class components, and UI components can be developed independently. These components can then be reused and nested inside each other to create the entire interface. So, you can build UI progressively and maintain code in a much better way.
Another reason developers prefer React is that it doesn’t have a rigid setup. Developers can install required plugins for routing, styling, state management, or API handling.
In the next section, let’s cover the technical benefits of React and why it is in high demand.
Core Technical Benefits of React
Large enterprises, such as Facebook, Netflix, Airbnb, Shopify, Walmart, PayPal, Instagram, and Uber, use React to develop most of their UI. All these companies embraced React because of its modularity, efficiency, and potential to run on both web and mobile fronts.
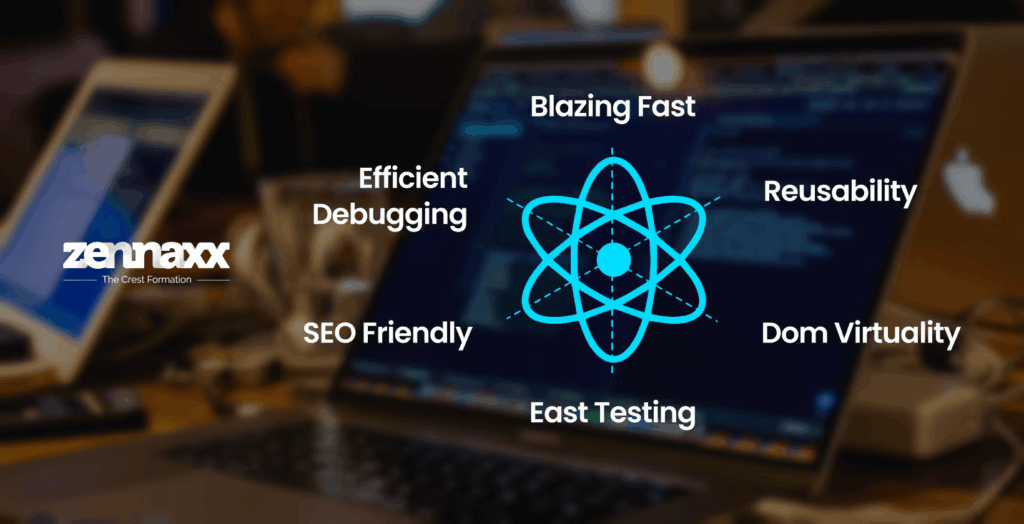
Some of the reasons why React is a top choice for front-end development are:
Component-Based Architecture & Reusability
React separates the UI into separate, reusable components. You can compartmentalise logic and style per component. This makes duplication a lesser concern, testing easier, and development faster when you scale.
Virtual DOM, Diffing & Reconciliation
React maintains a light, in-memory representation of the DOM (the Virtual DOM). When the state or props change, React creates a brand new Virtual DOM tree and compares it to the old one (diffing) before rendering only those sections that mismatch (reconciliation). The expensive operation of manipulating the real DOM is thus minimized.
Declarative Syntax: JSX, State & Props
JSX allows you to specify how the UI should appear in each state. State stores data within components. Props transfer data downward from parents. Whenever state or props are changed, React re-renders impacted components. This simplifies UI logic to read and maintain.
Unidirectional Data Flow
Data flows from parent components to children. This predictable direction simplifies debugging. It avoids the propagation of surprises in child components back up, maintaining component interactions in a simpler form.
Recent Improvements: Hooks, Concurrent Mode, Server Components, and Hydration
Hooks enable function components to control state and side effects in a clean manner. React’s Concurrent Mode (in React 18+) enables React to prioritize critical updates and suspend less critical work. Server Components minimise client bundle size by rendering in parts on the server. Hydration adds interactivity to server-rendered markup.
Community Strength & Learning Resources
React has millions of users globally. Its GitHub repository reflects millions of downloads per week and numerous stars. There are lots of forums provided by the React community: React.dev, Stack Overflow, Reddit, and Discord channels. Tutorials, courses, and documentation are out there in abundance.
Flexibility & Compatibility
You get to choose what routing, styling, backend, or state tool to employ. React gets along fine with REST APIs, GraphQL, server frameworks, or micro-frontends. It plays nicely with other tech stacks and lets you customise architecture instead of adhering to a strict one.
Use Cases of React

Some practical applications where developers use React are:
- Enterprise Web Applications: React is the backbone for developing enterprise-level web applications. Companies like Netflix, PayPal, and Shopify use React to develop UI and serve users under heavy traffic. With its modular design and robust ecosystem, scaling is significantly easier within larger teams and across multiple product lines.
- Cross-Platform Mobile Applications: React Native enables combining the functionalities of React and reusable code to build applications for iOS and Android simultaneously. The overall cost of creating applications is thus reduced. The time taken to deliver the project for both platforms is reduced as well.
- E-Commerce Platforms: React works great for an e-commerce site. It can handle real-time updatable contents such as product filtering, cart updates, and checkout flows without any lagging downtime. Using frameworks such as Next.js, React can handle SEO-heavy cases such as product pages.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): React can be used for the development of PWAs that work offline, send push notifications, and look like native apps on mobile devices while being delivered through the web.
Trade-offs, Challenges and Limitations of React
React provides a high degree of flexibility combined with very high performance. However, there are some trade-offs. Understanding the trade-offs will help teams to find out if React JS Web Development Services is the right choice for front-end development.
- Bundle Size & Initial Load: For large projects, shipping most of the React applications comes with heavy JavaScript bundles. This becomes a drag on first-page loads and can affect user experience. You can counter it with techniques like lazy loading, code splitting, and server-side rendering.
- Learning Curve for Advanced Features: React basic concepts are easy to grasp, but advanced use takes expertise. They include concurrent rendering, server-side rendering, or hydration. This can make it harder for teams with mixed skills to use React.
- Overkill for Small Apps: React is crazily overkill for small static sites or trivial applications. Svelte or even plain JavaScript can do things easily without React.
Best Practices for the Right Use of React
What follows are some measures to get the best from React:
Use Functional Component and Hooks
Preferably, use function components instead of class components. Use native hooks like useState, useEffect, useMemo, and useCallback to make state logic and side effects easier to manage. Hooks also allow you to avoid some of the general pitfalls related to class lifecycle methods.
Implement Lazy Load, Code Split and Rendering Strategy
Use lazy loading for anything not requiring it to be loaded during First Page Load. Use React.Lazy + Suspense or dynamic import for code splitting. Use SSR, SSG, or hybrid rendering when needed.
Optimize State Architecture and Unnecessary Renders
Store your state as close to the component using it as possible. In addition, memo, useMemo, and useCallback should be used to avoid child component re-renders when it’s not necessary. Avoid deep nesting or shared global states when possible.
Follow Progressive Enhancement
Design UI with basic elements first. Once you test that navigation and forms work on simple browsers and slow connections, go ahead and add advanced UI features one by one. This progressive enhancement ensures the reliability of the UI.
Conclusion

React is one of the best ecosystems for front-end development, which is why it has been popular among developers for more than a decade. As discussed in this blog, the components-based structure of direct DOM style, flexible project ecosystems, and a booming community accessing various support tools and libraries are some of the reasons behind its popularity.
If you are planning to develop a scalable application with a Modern UI interface, React can be the best choice.
Furthermore, if you are looking for the right partner for React JS Web Development Agency, Zennaxx Technology can be the best choice. We have delivered more than 700+ projects across multiple countries, and have an in-house team of 50+ people.
FAQs
- Is React a framework? React is a JavaScript library, not a framework. The choice is totally up to you concerning routing, data-fetching, or app structure.
- Do you need Redux every time? No. Redux is not yet compulsory to use. Redux is needed when the state becomes complex or scattered. Otherwise, you can use React State, Context API, or simple hooks.
- Is React useful for large enterprise-scale applications? Yes. Many enterprises, like Netflix, Walmart, PayPal, Shopify, and the like, rely on React. It is scalable and flexible, but with increasing complexities in the application, adequate optimization and state management become important.
- How to optimize performance in React applications? Follow these tips:
- Use lazy loading for heavy components
- Load only what’s needed with code splitting
- Use memoisation to avoid re-rendering
- Pre-render on server using SSR and SSG
- Keep state as close as possible to the component


