Web application development is the process of building software applications that run in web browsers and allow users to perform interactive tasks such as online purchasing, document editing, and data analysis. The web application development process focuses on cross-platform accessibility, fast deployment, and seamless integration with real-time data systems. The main steps involved in web application development include requirement gathering, UI/UX design, frontend and backend development, API integration, system testing, deployment, and post-launch maintenance. Web application development steps ensure that the final application is secure, scalable, and aligned with business goals.
The main programming languages for web application development include JavaScript, Python, PHP, Java, and TypeScript. The main frameworks used in web application development include Angular, Django, Laravel, Spring Boot, and Express.js. Web application development and mobile app development follow similar stages, including prototyping, coding, testing, and deployment. Web application development targets browser-based platforms and requires no installation, whereas mobile app development involves native or hybrid builds distributed through app stores.
The average cost of web application development ranges from $15,000 to $80,000, depending on the complexity, features, technology stack, and location of the development team. Developer rates range from $50 to $150 per hour, with additional expenses for UI/UX design, API integration, hosting, and ongoing maintenance.
The web application development industry is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.2% from 2024 to 2030. 60% of businesses prioritize web applications over traditional software, and progressive web applications (PWAs) increase user engagement by 50% compared to standard websites.
What Is Web Application Development?
Web application development is the end-to-end process of creating software applications that run inside web browsers and allow user interaction, real-time functionality, and secure data management. Web applications execute logic on both the client-side (frontend) and the server-side (backend) to deliver dynamic, interactive experiences. Custom web app development is the process of designing and building a specific web application that fulfills the requirements of a particular business problem, workflow, or operational need, and utilizes unique features, architecture, and user interfaces.
Developers build custom web applications from scratch using frameworks such as Laravel, Django, or Spring Boot to match exact workflows, security requirements, and scalability goals. A custom web application approach ensures full control over features, design, third-party integrations, and future upgrades. Custom web applications in healthcare, education, logistics, and financial technology are developed to meet the requirements of data protection regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Listed below are the main steps of the web application development process.
- Define web application goals and user problems
- Research web application market and audience
- Gather web application requirements and features
- Plan web application architecture and workflows
- Design web application UI and user experience
- Prototype and validate web application functionality
- Develop web application frontend and backend
- Integrate web application APIs and databases
- Test and optimize web application performance
- Deploy, monitor, and maintain web application
1. Define Web Application Goals and User Problems
Defining the web application goals and user problems means identifying what the web application must achieve and pinpointing the specific challenges users face in their current workflow. The goal-setting process ensures that the web application solves verified problems rather than assumptions. Developers conduct structured stakeholder interviews to gather detailed insights from project sponsors, customer service agents, sales teams, and other operational roles. Developers create user journey maps and personas that connect each challenge to a specific business process, ensuring that every identified problem reflects actual user friction.
A McKinsey Digital study from 2023 found that software projects that begin with well-defined objectives and documented user problems are 1.5 times more likely to succeed than projects that skip early-stage problem validation. Setting specific goals based on actual user friction reduces unnecessary rework, shortens development cycles, and improves the chances of delivering a product that solves measurable business challenges.
The best practices for defining the web application goals and user problems in the web application development step include aligning every goal with performance indicators that reflect user impact and system efficiency. The performance indicators for defining the web application goals and user problems include outcomes such as “reduce order assignment time by 70%” or “decrease support ticket volume by 40%.” Developers validate user behavior for each problem using analytics platforms such as Google Analytics, Hotjar, or FullStory to ensure that behavioral data supports every problem.
Examples of defining web application goals and user problems include a delivery management company that sets the goal “automate real-time dispatch using GPS tracking” to solve delayed manual order assignment. Another example of defining web application goals and user problems is a hospital system that establishes the goal of users to address limited access to patient reports.
2. Research Web Application Market and Audience
Researching the web application market and audience means gathering verified insights about user behavior, competitor features, and demand trends to support strategic product decisions. Product analysts and developers perform web application research by studying user demographics, platform preferences, and usage patterns across the target market. The web application research process includes analyzing existing solutions, identifying gaps in competitor offerings, and observing how users interact with similar platforms.
The best practices for researching the web application market and audience include identifying user segments, conducting competitor benchmarking, and validating needs through interviews, surveys, or public datasets. Reliable performance indicators for the web application research phase include metrics such as percentage of mobile-first users, top-requested feature categories, or average session abandonment rate. Developer teams validate web application research findings using tools (Google Trends, Similarweb, Statista, direct user feedback) and through platforms (Typeform, Hotjar).
Examples of valuable market insights include identifying that enterprise users prefer mobile dashboards, that competitors lack role-based access control, or that target users frequently abandon existing tools due to poor load times.
3. Gather Web Application Requirements and Features
Gathering web application requirements and features means documenting the technical, functional, and user-facing capabilities that the web application must include to achieve its intended outcomes. Gathering web application requirements and features ensures that the web application development process begins with clear expectations, prevents scope creep, and promotes structured collaboration between technical and business teams. Product analysts and developers gather web application requirements and features by working directly with stakeholders, conducting structured workshops, and converting business needs into detailed technical specifications.
The best practices for gathering web application requirements and features include identifying use cases for every user type, documenting each feature’s priority level, and breaking down requirements into modular deliverables. The performance indicators for the gathering web application requirements phase include the number of validated features, feature prioritization scores, and stakeholder approval rate. Development teams validate web application requirements and features using requirement traceability matrices, feedback loops during sprint planning, and confirmation from end-user testing or mockup reviews.
Examples of web application requirements and features include multi-user access control for enterprise permissions, offline form submission to support remote field teams, and real-time notifications to keep users updated on workflow progress.
4. Plan Web Application Architecture and Workflows
Planning web application architecture and workflows means designing the foundational structure, data movement, and user interaction patterns that define how the web application operates. Planning web application architecture and workflows ensures that the system remains scalable, secure, and maintainable as user needs evolve and complexity increases. Developers plan web application architecture and workflows by defining how frontend components communicate with backend services, organizing database models, and visualizing the sequence of user actions from login to task completion.
The best practices for planning web application architecture and workflows include selecting architecture patterns based on project size and flexibility needs, separating concerns across layers, and maintaining clear API contracts. The performance indicators for planning web application architecture and workflows include system response time benchmarks, load-handling capacity under simulated traffic, and the reusability of modular components across features. Development teams validate web application architecture and workflows using technical documentation, prototype testing, performance simulation tools ( JMeter, Postman), and review sessions with cross-functional teams.
Examples of web application architecture and workflows include choosing microservices over monolithic design to improve scalability, using RESTful APIs to streamline service communication, and designing approval workflows for multi-level user roles in enterprise systems.
5. Design Web Application UI and User Experience
Designing web application UI and user experience means creating user-friendly interfaces that follow accessibility standards, visual consistency, and real-world usage behavior. UI/UX designers and frontend developers design web application UI and user experience by building wireframes, defining layout grids, and mapping out interaction flows for everyday user actions. Design teams apply style guides and component libraries to maintain consistency and improve ease of use throughout the web application interface.
The best practices for designing web application UI and user experience include using mobile-first responsive layouts, following WCAG accessibility guidelines, and maintaining visual consistency through a shared design system. The performance indicators for designing web application UI and user experience include user satisfaction scores, form completion rates, and reduction in user drop-offs during key flows. Design teams validate web application UI and user experience through usability testing, A/B experiments, and real-time session recordings using tools such as Figma, Maze, or Hotjar.
Examples of essential UI/UX elements include responsive layouts for mobile access, consistent form controls for input validation, and visual cues such as progress indicators for task completion feedback.
6. Prototype and Validate Web Application Functionality
Prototyping and validating web application functionality means building interactive models to test core workflows, verify usability, and collect early user feedback before full-scale development begins. Frontend developers and UI/UX designers prototype and validate web application functionality by creating interactive wireframes, HTML mockups, or clickable Figma flows.
The best practices for prototyping and validating web application functionality include building prototypes for all high-traffic workflows, prioritizing usability testing, and recording insights from both internal stakeholders and external testers. The performance indicators for prototyping and validating web application functionality include user error rates during testing, average task completion time, and the number of validated user journeys. Design and development teams validate web application functionality using usability testing sessions, click-tracking tools, and prototype review platforms such as Maze, Figma, or UserTesting.
Examples of prototyping and validating web application functionality include testing a multi-step onboarding form to identify user drop-off points, simulating e-commerce checkout flows to detect potential errors, and refining dashboard filters based on tester feedback.
7. Develop Web Application Frontend and Backend
Developing a web application frontend and backend means building the visual interface and server-side logic that power the web application’s complete functionality and responsiveness. Frontend developers and backend developers develop web application frontends and backends by implementing interactive components using frameworks (Vue.js, React), and data management logic using technologies (Laravel, Node.js, Django).
The best practices for developing web application frontends and backends include separating concerns between presentation and logic, ensuring API security with authentication and rate-limiting, and writing reusable, well-documented code. The performance indicators for developing web application frontend and backend include API response time, frontend load time, error-free deployments, and code coverage in automated tests.
Examples of developing web application frontend and backend include creating a dynamic product listing page with real-time filters, building a secure login system with two-factor authentication, and integrating backend APIs to display live user activity on dashboards.
8. Integrate Web Application APIs and Databases
Integrating web application APIs and databases connects the application to external services and internal data storage systems for real-time functionality and persistent data flow. Integrating web application APIs and databases ensures that users can access live information, perform transactions, and interact with third-party systems without disruption. Backend developers and integration engineers integrate web application APIs and databases by configuring RESTful or GraphQL endpoints, managing relational or NoSQL database schemas, and setting up secure data pipelines.
The best practices for integrating web application APIs and databases include enforcing authentication on all API calls, normalizing database structures, and logging all data transactions for auditability and debugging. The performance indicators for integrating web application APIs and databases include query execution time, successful API call rates, and latency in data synchronization. Development teams validate web application API and database integrations using test suites, API monitoring tools, database query profilers, and staging environments with simulated data loads.
Examples of integrations include connecting Stripe for payments, using Firebase for real-time messaging, and linking a PostgreSQL database to manage user records and transactions.
9. Test and Optimize Web Application Performance
Testing and optimizing web application performance ensures the system runs reliably under various usage conditions, delivering a fast and stable experience. Testing and optimizing web application performance ensures that users experience fast load times, minimal errors, and consistent functionality across devices and network speeds. Quality assurance engineers and developers test and optimize web application performance by performing unit testing to verify individual components, integration testing to validate system interactions, and load testing to measure system behavior under traffic stress.
The best practices for testing and optimizing web application performance include running automated test suites during each deployment, setting response time thresholds for critical pages and APIs, and proactively identifying memory. The performance indicators for testing and optimizing web application performance include API response time, frontend load time, error rates, and throughput under concurrent requests. Development teams validate web application performance using tools such as Apache JMeter, Google Lighthouse, Postman, and New Relic to simulate usage, profile bottlenecks, and monitor real-time performance.
Examples of performance optimization include reducing API response delays through caching, compressing frontend assets to decrease load times, and profiling database queries to eliminate bottlenecks.
10. Deploy, Monitor, and Maintain Web Application
Deploying, monitoring, and maintaining a web application involves launching it to a live environment and ensuring it remains secure, stable, and updated over time. Deploying, monitoring, and maintaining a web application ensures that users receive a stable, up-to-date experience while development teams can respond quickly to bugs, performance issues, and system updates. DevOps engineers and developers deploy, monitor, and maintain web applications by setting up CI/CD pipelines for automated deployment, configuring monitoring dashboards, and applying version-controlled patches and feature rollouts.
Best practices for deploying, monitoring, and maintaining a web application include enforcing zero-downtime deployment strategies, enabling automated health checks, and scheduling regular audits to assess code quality and infrastructure vulnerabilities. The performance indicators for deploying, monitoring, and maintaining a web application include uptime percentage, mean time to recovery (MTTR), system error rate, and the number of successful deployment cycles. Development teams validate deployment and maintenance workflows using tools such as GitHub Actions, Jenkins, Sentry, New Relic, and Prometheus to track live errors, monitor server metrics, and manage version control.
Examples of maintenance tasks include deploying a hotfix for a security vulnerability, monitoring server load during traffic spikes, and updating deprecated API endpoints after third-party changes.
What Software Are Used for Web Application Development?
Web application development software refers to the set of tools, languages, and platforms used to build, test, and deploy functional, interactive web-based systems. Web application development tools include programming languages, development frameworks, and integrated development environments (IDEs) that developers use throughout the software development lifecycle.
- Programming Languages Used in Web Application Development
- Frameworks Used in Web Application Development
- Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) for Web Application Development
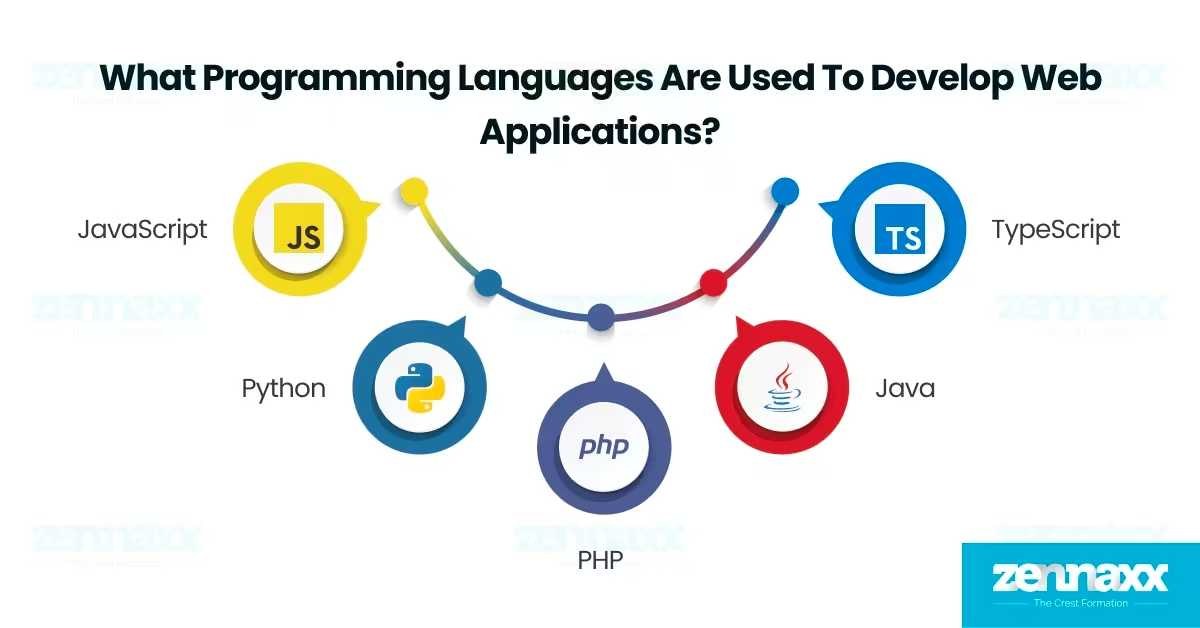
What programming languages are used to develop web applications?
Listed below are the 5 programming languages to develop web applications.
1. JavaScript
JavaScript is used in web application development to build interactive, real-time user interfaces that run directly in the browser. Developers use JavaScript in web application development to handle events, execute asynchronous operations, and manipulate the DOM. JavaScript has remained the most widely used language in web application development for 11 consecutive years, adopted by over 65% of developers due to its native browser support and extensive ecosystem (2023 Stack Overflow Developer Survey).
2. Python
Python is used in web application development to build scalable backend systems, automate workflows, and process data-intensive operations. Developers use Python in web application development with frameworks (Django, Flask) to implement clean, modular code, user authentication, and API logic. According to the 2023 JetBrains Developer Ecosystem Survey, Python ranks among the top 3 languages used in web application development due to its extensive libraries, rapid development capabilities, and native support for machine learning integrations.
3. PHP
PHP is used in web application development to power server-side logic, generate dynamic content, and manage relational databases. Developers use PHP in web application development with platforms such as Laravel or native PHP to connect to MySQL, handle user sessions, and process form data securely. According to W3Techs, PHP is used by over 76% of all websites with known server-side languages, making it foundational for content management systems, e-commerce portals, and custom backend development.
4. Java
Java is used in enterprise-level web application development to build secure, high-performance backend services across large-scale systems. Developers use Java in web application development with tools (Spring Boot, Hibernate) to create REST APIs, manage transactions, and ensure cross-platform deployment. According to Oracle and Statista, Java continues to power over 30% of enterprise web application development due to its robust memory management, scalability, and long-term ecosystem support.
5. TypeScript
TypeScript is used in modern web application development to add static typing and advanced tooling to JavaScript-based projects. Developers use TypeScript in web application development to write maintainable code, detect type errors early, and enhance collaboration across large teams using frameworks (Angular, React, Vue). According to the 2023 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, TypeScript is adopted by over 40% of developers for web application development due to its reliability and seamless integration with frontend stacks.
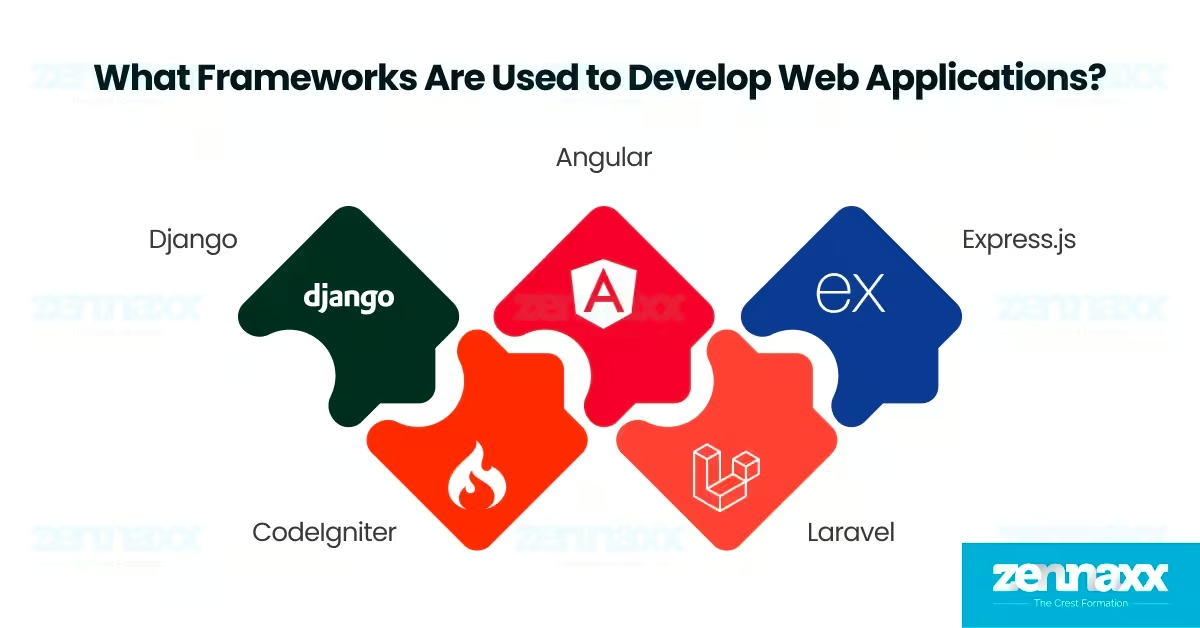
What Frameworks Are Used to Develop Web Applications?
Listed below are the 6 popular web app development frameworks.
- Angular: Angular is used in web application development to build dynamic, client-side applications using TypeScript. Developers choose Angular for its built-in support for two-way data binding, dependency injection, and component-based architecture, making it ideal for large-scale single-page applications (SPAs).
- Django: Django is used in web application development to create secure and scalable backend systems in Python. Developers use Django’s built-in tools for authentication, ORM-based database access, and URL routing to accelerate development while maintaining high-security standards.
- Express.js: Express.js is used in web application development to build lightweight server-side applications using Node.js. Developers prefer Express.js for its minimalistic structure, fast routing, and flexibility when creating RESTful APIs and real-time microservices.
- Laravel: Laravel is used in web application development to streamline backend development using PHP and the MVC pattern. Developers benefit from Laravel’s clean syntax, built-in authentication, and modular components, which enable the creation of secure and feature-rich applications.
- CodeIgniter: CodeIgniter is used in web application development to deliver high-speed performance and simplicity in PHP-based projects. Developers choose CodeIgniter for its minimal setup, low footprint, and ease of building small-to-medium scale applications with pre-built libraries.
- React: React is used in web application development to build fast and interactive user interfaces. Developers use React’s component-based model and virtual DOM to render real-time UI updates in single-page and mobile-responsive applications.
React is the most widely used framework among web application frameworks in
web application development, and valued for its fast rendering, modular design, and seamless integration with modern frontend stacks.
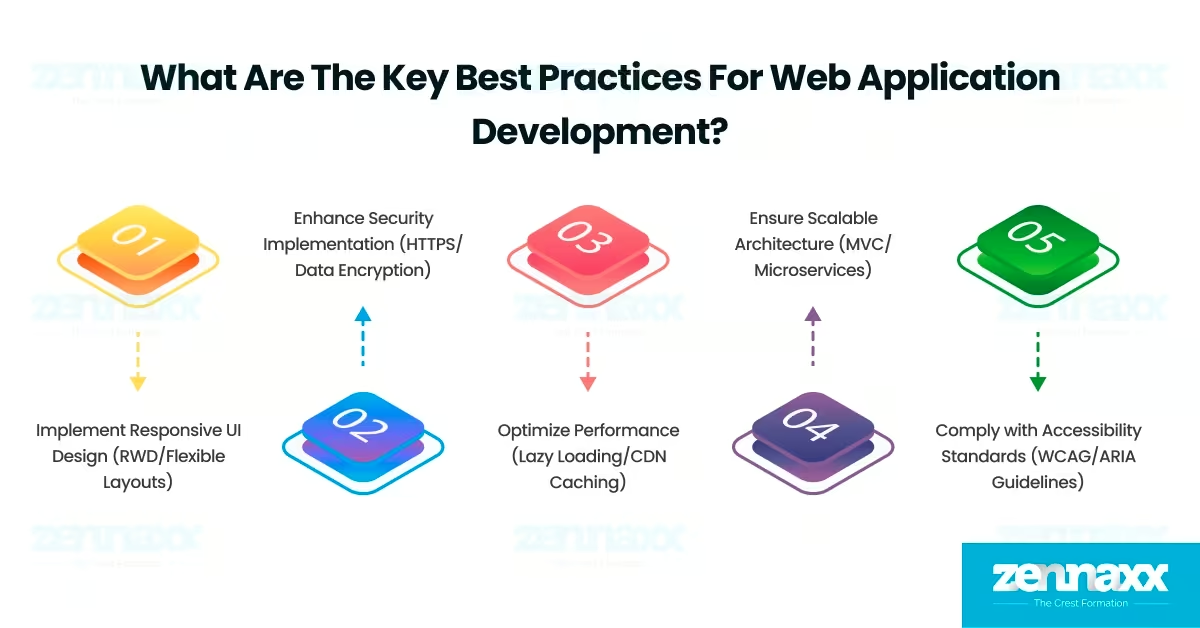
What are the key best practices for Web application development?
The key practices for web application development include responsive design, security implementation, performance optimization, scalable architecture, and SEO-friendly development to ensure a fast, secure, and user-friendly experience.
Listed below are 5 best key practices for web application development.
- Implement Responsive UI Design (RWD/Flexible Layouts): Responsive UI design ensures a seamless user experience across different screen sizes and devices. Responsive UI design is necessary for 90% of web applications, as mobile devices account for over 60% of global web traffic. Applying responsive UI design requires using Responsive Web Design (RWD) techniques, configuring viewport meta tags for adaptive scaling, and structuring CSS with flexible grid layouts.
- Enhance Security Implementation (HTTPS/Data Encryption): Security implementation protects web applications from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Security implementation is mandatory for 100% of web applications, as 43% of cyberattacks target web-based platforms. Strengthening security implementation involves applying end-to-end encryption and enforcing authentication protocols to prevent data breaches.
- Optimize Performance (Lazy Loading/CDN Caching): Performance optimization improves loading speed and responsiveness in web applications. Performance optimization is crucial for 80% of web applications, as 40% of users abandon slow-loading websites within 3 seconds. Improving performance requires applying lazy loading for images and scripts, optimizing Content Delivery Network (CDN) caching, and reducing HTTP requests to decrease page load time.
- Ensure Scalable Architecture (MVC/Microservices): Scalable architecture maintains web application stability and flexibility as user demand increases. Scalable architecture is necessary for 85% of web applications because high-traffic websites require well-structured frameworks to handle growth. Implementing scalable architecture involves using Model-View-Controller (MVC) patterns, developing microservices-based backend structures, and applying modular coding practices.
- Comply with Accessibility Standards (WCAG/ARIA Guidelines): Accessibility compliance ensures inclusivity for users with disabilities. Accessibility compliance is essential for 70% of web applications because global regulations require web platforms to meet accessibility standards. Meeting accessibility compliance involves implementing ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) attributes and using semantic HTML for screen reader compatibility.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Web Application?
The cost of web application development starts at $15,000 and goes up to $80,000, with developer rates ranging from $50 to $150 per hour. Web application development cost also includes charges for design, API integration, hosting, and ongoing maintenance to ensure the application functions effectively. The final price of web application development is influenced by the app’s complexity, features, technology stack, and the location of the development team.
What factors should be considered before hiring a web development agency?
You should consider factors before hiring a web development agency are experience, technology stack, cost, communication, and security compliance. A
web app development company should have a strong portfolio, expertise in modern frameworks, transparent pricing, and effective project management to ensure timely delivery. Security measures, including data protection, secure coding, and compliance with industry standards, should also be prioritized to ensure a reliable and scalable web application.
What IDEs Are Used for Web Application Development?
IDEs used for web application development provide integrated environments for writing, debugging, and managing code across frontend and backend layers.
Listed below are the 5 IDEs used for web application development.
- Visual Studio Code: Visual Studio Code is an IDE used in web application development for lightweight, extensible coding with strong support for JavaScript, TypeScript, and HTML.
- JetBrains WebStorm: JetBrains WebStorm is an IDE used in web application development that provides intelligent code completion and smooth integration with frontend frameworks such as React and Angular.
- Eclipse: Eclipse is an IDE used in web application development for building Java-based and enterprise-grade applications with Web Tools Platform (WTP) support.
- NetBeans: NetBeans is an IDE used in web application development that supports multiple languages, including Java, PHP, and JavaScript, with built-in project management features.
- PhpStorm: PhpStorm is an IDE used in web application development for advanced PHP coding, real-time debugging, and front-end integration in complex backend projects.
Are web applications developed in the same way as other mobile apps?
No, web applications are not developed in the same way as other mobile applications. Web applications run in web browsers using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Technologies. The mobile applications can be developed using platform-specific IDEs such as Android Studio or Xcode. The development principles are the same for web applications and other mobile applications.
Mobile app development requires creating separate versions for Android and iOS, whereas web applications are platform-independent and are accessed across multiple devices without installation.
How much time does it take to develop web applications?
The time required to develop native applications ranges from 3 to 9 months, with simple applications taking around 3–4 months and complex applications requiring 6–9 months or more. The development duration depends on app complexity, feature set, platform (iOS or Android), UI/UX design, backend integration, and team expertise.