
An iOS app, or iOS application, is a software program designed to operate on Apple devices running the iOS operating system, such as the iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch. iOS applications are packaged, signed, and distributed exclusively through the Apple App Store, which hosts approximately 2.095 million active apps as of mid‑2025, including around 380,000 games (Business of Apps, 2025).
The components of an iOS app are structured into 4 modular system layers, each layer is responsible for different areas of functionality. The components of an iOS app include the Core OS layer, the Media layer, the Cocoa Touch layer, the UIKit or UI elements, and the Architectural patterns. The features of iOS applications are centered around usability, reliability, functionality, efficiency, Model-View-Controller (MVC) Architecture, native development, data-driven design, and security.
iOS applications run natively on three categories of Apple devices: the iPhone, the iPad, and legacy models of the iPod Touch. The pros of iOS applications include high revenue potential, advanced security, and a stable development environment. The limitations of iOS applications primarily relate to the lack of customization control, development environment constraints, and limited global scalability. Apple enforces strict developer policies that limit access to certain APIs, disallow background execution in most cases, and mandate adherence to uniform UI patterns defined in its Human Interface Guidelines.
What is an iOS Application?
1. What Is an iOS Operating System?
The iOS (<span”>iPhone Operating System)<span”> is a Unix-based mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc. to power its consumer hardware (iPhone, iPad (until 2019), and iPod Touch (until 2022)). iOS is used exclusively on Apple devices and cannot be installed or operated on Android smartphones or third-party hardware.
Apple introduced the iOS operating system during the unveiling of the first-generation iPhone on January 9, 2007, at Macworld San Francisco, led by Steve Jobs. The original version of iOS, known internally as iPhone OS 1.0, supported only pre-installed Apple apps and lacked features such as copy and paste and support for third-party apps. The current stable release of the iOS operating system is iOS 18, launched on September 16, 2024, according to Apple’s official Release Notes. Apple released iOS 18.6 beta 1 as part of its developer preview cycle to offer incremental updates and feature refinements under the Apple Beta Software Program on June 16, 2025. iOS 18 features redesigned Control Center widgets, enhanced Siri functionality, improved privacy controls, and app-specific locking features utilizing Face ID.
2. What Are the Examples of iOS Applications?
- FaceTime
- Find my Apple Music
- Apple TV
- iMessage
- Apple Podcasts
- Measure
- Compass
- Reminders
- Health
- Wallet
What Is the File Format of iOS Applications?
The file format of iOS applications is .ipa, which stands for iOS App Store Package. An .ipa file is a compressed archive that contains the compiled app binary, resource assets, executable code, entitlements, and digital signatures required for application installation and execution on Apple devices. iOS and iPadOS platforms use the .ipa format to distribute applications on iPhones and iPads through the App Store and approved developer workflows.
The .ipa files can be installed on every iOS device if the device satisfies Apple’s compatibility rules (iOS version support, signed app validation, and Apple ID authentication). Apple does not allow standard users to install .ipa files manually through drag-and-drop or external transfer methods. iPhones and iPads that are not enrolled in the Apple Developer Program or TestFlight cannot sideload .ipa files unless connected to Xcode through a macOS environment.
What are the Components of iOS Applications?

The 4 core components of iOS applications are the Core OS layer, Core Services layer, Media layer, and Cocoa Touch layer.
- Core OS Layer in iOS Applications:
The Core OS layer in iOS applications controls system-level operations such as memory allocation, CPU thread scheduling, device boot sequencing, and hardware-level security enforcement. The XNU kernel of the core OS layer blends the Mach microkernel with components from BSD Unix, provides low-level system calls and manages process isolation across applications. The Apple Security Framework in core OS layer enforces code signing, sandboxing, and keychain-based encryption to ensure that applications cannot access unauthorized memory or data. The POSIX-compliant runtime environment embedded within the Core OS layer allows developers to utilize standardized system commands for file operations, process management, and thread control, facilitating compatibility with Unix-based development tools. - Core Services Layer in iOS Applications:
The Core Services layer of iOS applications provides frameworks that support application logic and data handling across Apple devices. The components of the core service layer include Foundation Framework, Core Data, and CloudKit, which allow developers to manage data persistence, in-app purchases, and iCloud storage. The Core service layer enables geolocation with Core Location, background task execution with Grand Central Dispatch (GCD), and seamless communication via NSURLSession. The Core services ensure that iOS applications operate with real-time responsiveness and secure network access. - Media Layer in iOS Applications:
The Media layer in iOS applications manages multimedia experiences by providing frameworks for image rendering, audio and video playback, and 3D graphics. Core frameworks in the media layer include AVFoundation, Core Animation, Metal, and Core Image. Developers use the media layer to enable live video streaming, augmented reality (via ARKit), custom audio effects, and smooth UI transitions. iOS Applications such as Apple Music and FaceTime depend on the media layer to deliver immersive and high-fidelity content. - Cocoa Touch Layer in iOS Applications:
The Cocoa Touch layer of iOS applications delivers the primary user interface and interaction frameworks. Cocoa Touch’s topmost layer includes UIKit, MapKit, PushKit, and Notification Centre services. iOS applications use Cocoa Touch to manage gesture-based input (such as swipes and taps), view hierarchies, touch animations, and modal navigation. The Cocoa Touch layer supports data persistence through UserDefaults and integrates smoothly with system events and hardware sensors to provide a polished user experience across iPhones and iPads.
1. What Are the Features of iOS Applications?
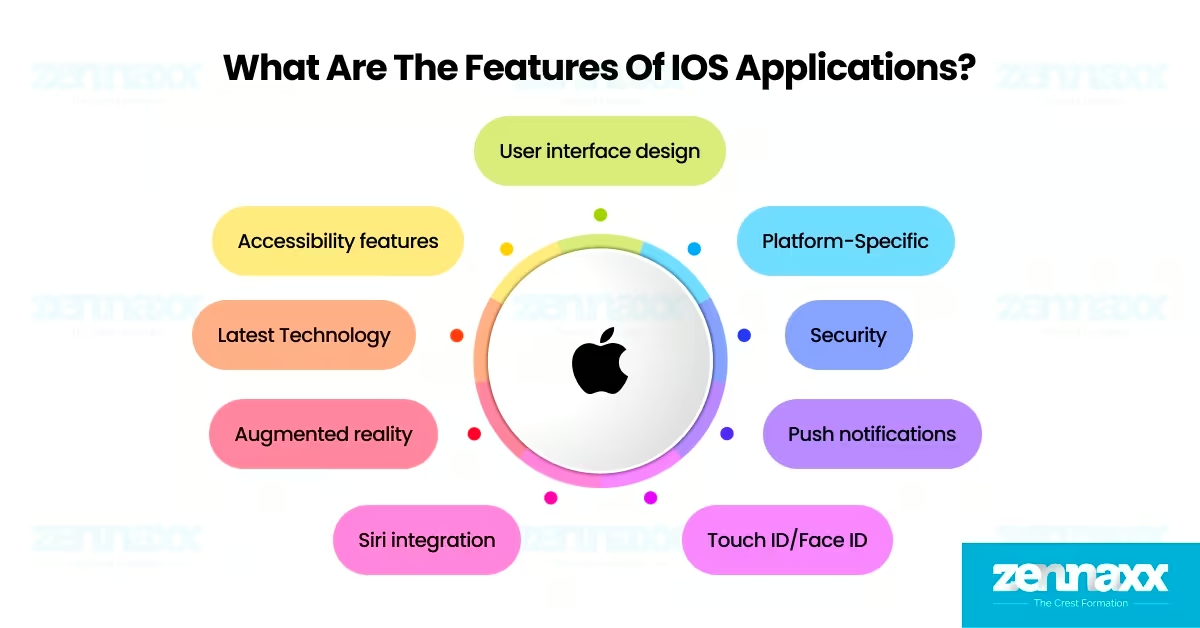
The features of iOS applications represent a combination of platform-level capabilities, secure architecture, and design consistency that differentiate iOS applications from applications built for other mobile operating systems.
- Native Development with Apple Tools: Native development with Apple tools allows iOS application developers to build software using Swift and Objective-C within Apple’s official development environment, including Xcode and Interface Builder. Native development with Apple tools enables low-level access to system APIs, efficient memory management, and direct hardware acceleration.
- Tight Integration with Apple Ecosystem: The feature of tight integration with Apple’s ecosystem enables iOS applications to communicate directly with core Apple services (iCloud, Apple Pay, SiriKit, HealthKit). Tight integration with Apple’s ecosystem enables seamless user experiences across iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches by leveraging device sensors, encrypted communication protocols, and cross-device data continuity.
- Consistent User Interface Through MVC Architecture: The feature of a consistent user interface through Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture allows iOS applications to maintain a clean separation between the user interface (View), application logic (Controller), and data management (Model). The MVC architecture in iOS simplifies codebase maintenance, enhances testability, and enables developers to reuse interface elements across iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches.
- Media-Rich and Context-Aware Experience: The media-rich and context-aware experience feature in iOS applications enables developers to deliver immersive visuals and interactive functionality using Apple’s high-performance frameworks. Context-aware features utilize GPS, accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer data to offer personalized services in navigation apps, health monitoring tools, and fitness tracking platforms.
- Advanced Home Screen Customization: The advanced home screen customization feature in iOS applications enables users to personalize their interface through interactive widgets, Smart Stacks, and the App Library. iOS devices support dynamic widget resizing, context-based widget suggestions, and automated widget rotation using Apple’s WidgetKit framework.
- 6. Strong Security and Privacy Enforcement: Security enforcement in iOS applications requires every application to pass Apple’s manual App Store review process. The review ensures compliance with Apple’s data protection rules, including code-signing validation, sandbox isolation, and secure handling of user data. Privacy enforcement in iOS applications includes integration with App Tracking Transparency (ATT), restriction of access to the Identifier for Advertisers (IDFA), and user consent mechanisms for data sharing.
2. What Devices Support iOS Applications?
- iPhone 16 series: iPhone 16, iPhone 16 Plus, iPhone 16 Pro, iPhone 16 Pro Max
- iPhone 15 series: iPhone 15, iPhone 15 Plus, iPhone 15 Pro, iPhone 15 Pro Max
- iPhone 14 series: iPhone 14, iPhone 14 Plus, iPhone 14 Pro, iPhone 14 Pro Max
According to global device analytics and Apple’s Q1 2024 financial disclosures, Apple has sold over 2.3 billion iPhones worldwide, which makes the iPhone the dominant device class for iOS applications.
Where to Download an iOS Application?
- Tap the App Store icon on an iPhone or iPad device.
- Use the search bar to enter the name of the application.
- Tap the “Get” button next to the desired app listing.
- Authenticate the download using Face ID, Touch ID, or an Apple ID password.
- Wait for the installation to complete; the app icon will appear on the home screen.
What are the Pros of iOS Applications?
- Enhanced User Experience: iOS applications offer enhanced user experience by following Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines (HIG), which require intuitive, consistent, and minimalist design across devices such as iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches. Features such as smooth transitions, fast loading speeds, and gesture-based controls contribute to high usability across diverse user demographics.
- Fast and Secure System Integration: iOS applications enable fast and secure integration with Apple’s ecosystem services which includes iCloud, Apple Pay, Siri, Apple Health, and HomeKit. Users benefit from synchronized data across Apple devices through iCloud Handoff, which allows activities to smoothly transition between an iPhone, iPad, Mac, or Apple Watch without interruption.
- Regular Security and Feature Updates: iOS applications receive frequent updates aligned with Apple’s system-level releases. These iOS updates deliver security patches, API upgrades, and performance improvements. Developers are required to keep apps compatible with the latest iOS version, which reduces fragmentation and improves user security.
- Strict App Store Quality Control: iOS applications are distributed only through the Apple App Store, which uses a strict review process based on Apple’s App Store Review Guidelines. This controlled distribution in iOS applications minimizes malware risk and prevents low-quality or non-compliant apps from reaching users.
- Advanced Built-in Security Features: iOS applications benefit from advanced built-in security layers such as Face ID, Touch ID, keychain encryption, end-to-end encrypted messaging (in iMessage), and code-signing enforcement. These advanced features protect user credentials, ensure secure authentication, and block unauthorized access to sensitive data and system APIs.
- Hardware and Software Optimization: iOS applications are optimized for Apple’s hardware and software stack, which provides improved memory management, enhanced GPU performance, and increased energy efficiency. This native optimization results in lower crash rates and smoother animations compared to many cross-platform apps on Android.
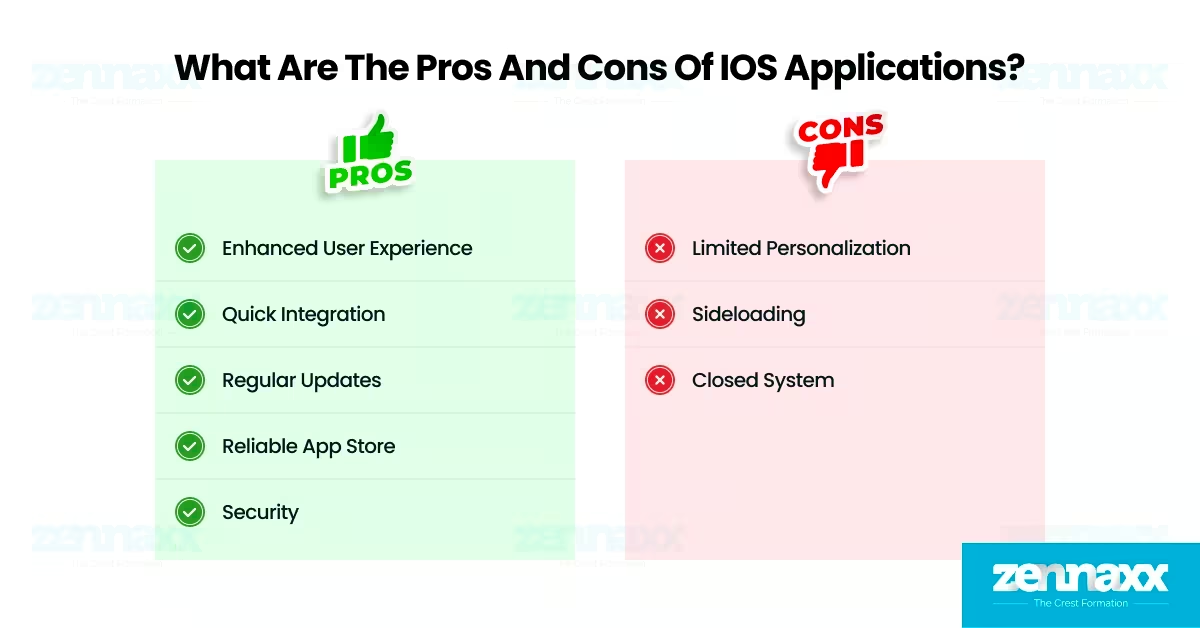
What Are the Cons of iOS Applications?
- Limited User Customization: iOS applications offer limited customization features such as icon packs, launcher themes, or deep UI personalization. Compared to Android devices, users cannot modify core visual elements, restrict app layout flexibility, or apply third-party skins.
- No Official Sideloading Support: iOS applications can only be downloaded through the Apple App Store, with no native support for sideloading or alternative app markets. This restriction limits user flexibility, unlike Android devices, which support multiple app sources such as Google Play, Samsung Galaxy Store, and APK-based installations.
- Closed Ecosystem Compatibility: iOS applications are restricted to Apple’s proprietary ecosystem, which includes iPhones, iPads, and Macs. Applications built for iOS are not compatible with non-Apple devices, which limits the potential reach for developers targeting a wider range of hardware diversity or cross-platform deployments.
- Strict Development and Publishing Requirements: iOS applications require compliance with Apple’s strict development tools (Xcode, Swift/Objective-C), and submission involves a detailed review process. Developers face longer approval timelines, higher publishing fees, and more rigid compliance checks compared to platforms with more open review policies.
How are iOS Applications Different from Other Types of Mobile Applications?
-
iOS Applications vs Progressive Web Applications (PWAs):
iOS applications are downloaded through the Apple App Store and support native system features (Face ID authentication, ARKit for augmented reality, CoreBluetooth for hardware-level connectivity). iOS applications are developed using Swift or Objective-C in Xcode and operate in a sandboxed environment that ensures strict memory isolation and full offline capability through Core Data and SQLite. Progressive Web Applications (PWAs) depend on service workers, cache APIs, and IndexedDB for limited offline access and lack integration with iOS-exclusive APIs. -
iOS Applications vs Android Applications:
iOS applications are developed using Swift or Objective-C in Xcode, while Android applications are built with Kotlin or Java in Android Studio. iOS applications follow Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines for consistent visual behavior across iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches. Android applications display varied user interfaces due to custom overlays such as Samsung One UI, Xiaomi MIUI, and Oppo ColorOS. iOS applications are installed only via the Apple App Store after undergoing a strict security review, whereas Android applications are distributed through Google Play or sideloaded from third-party sources, which increases the risks of malware and data leakage. -
iOS Applications vs Google Applications:
iOS applications are native to Apple’s ecosystem and integrate with services such as Siri, iCloud, and Apple Pay at the system level. Google applications (Gmail, Google Drive, YouTube) are cross-platform apps designed for Android, with secondary support for iOS. Google applications installed on iOS devices are confined to Apple’s sandbox architecture, which restricts their access to system-level features (background task execution, Bluetooth-based interactions, native API integration).
1. How Are iOS Applications Developed?
iOS applications are developed through a 5-phase process that includes planning, native development, user interface design, testing, and App Store deployment. The planning phase involves defining the application’s purpose, designing user flows, and preparing wireframes using tools like Figma or Sketch. Native development is carried out in Apple’s Xcode IDE using Swift and involves integrating iOS frameworks such as UIKit, CoreData, and AVFoundation for functional modules. The user interface is designed based on Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines to ensure visual consistency, responsiveness, and accessibility across devices such as iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches. Testing in iOS development company is performed on simulators and real devices using TestFlight to verify usability, fix bugs, and ensure compliance with App Store Review standards before final submission.
2. What Makes a Perfect iOS Development Company?
A perfect iOS development company demonstrates expert-level proficiency in Swift and Objective-C programming, along with deep familiarity with Apple’s iOS development ecosystem. A qualified team from an iOS development company utilizes frameworks such as UIKit for interface design, Core Data for local data storage, Core Animation for smooth transitions, and AVFoundation for media processing. An iOS development company operates within Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines and App Store Review Standards to ensure UI consistency, data privacy, and performance reliability. A perfect iOS development company consistently delivers stable, scalable, and user-centric applications within defined budgets and deadlines.


