Every SaaS company needs a proof of concept to prepare its product for launch. However, building a prototype can be challenging at an economic and operational level.
Developing a full-fledged prototype can cost $50,000 and beyond. This is where MVP development can help.
MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, allows you to build a shippable version of your SaaS product.
This means you don’t need to spend money on building all the features and functionalities of SaaS products.
You can focus on core functionalities for the MVP building process and collect usage feedback to improve the product experience.
So, how can you build an effective MVP for your SaaS product?
This article focuses on different aspects of MVP development, from its types to a step-by-step process for building it and the need to pivot a SaaS product. First, let’s understand what an MVP is!
What is a Minimum Viable Product?
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the basic version of a product that allows feedback accumulation for iterative Improvements. So, you launch a product with minimal and most needed features.
Users experience these features and provide feedback, which you can incorporate to make continuous improvements.
Eric Ries first coined the term “Minimum Viable Product” in his book The Lean Startup. According to Ries, an MVP is a version of a new product that allows teams to collect maximum validated learning from customers with the least effort.
The main idea behind MVP development is to test your SaaS product or service, ensuring maximum feedback to improve the user experience with each iteration.
MVPs can be prototypes, landing pages, videos, or even emails. While MVP development can be used to understand how a SaaS product works, other use cases exist.
First, you need to remember that not all MVPs become full-blown businesses. Entrepreneurs leverage the MVP-building approach to validate whether an idea may work.
If it’s not viable, the idea is often dropped. Similarly, many major tech giants and enterprises have leveraged this approach to reduce the cost and time needed for initial deployments.
Examples of Minimum Viable Products
Minimum Viable Products, or MVPs, have been pivotal for many businesses across domains in gathering essential insights into how customers use them. However, the word “product” in MVP is not entirely relevant.
As Steve Cohen once said, businesses should refer to experimentation instead of product. But why so? Dropbox’s MVP has all the answers!
1) Dropbox
Dropbox’s transition from an MVP to a leading cloud storage platform was more than experimentation.
In 2011, Dropbox’s MVP introduced file synchronization and sharing across multiple devices.
However, the most exciting story is where Drew Houston used a video to showcase the synchronization features of Dropbox MVP.
This helped the brand increase the number of beta testers from 5000 to 75000. Dropbox’s MVP required no complex setup, making it user-friendly for beta testers.
With newer iterations, Dropbox introduced new features based on user feedback and market demands.
This approach enabled Dropbox to minimize development time and resources while meeting user needs.
2) Zappos
Zappos, the popular online shoe retailer, used a concierge MVP to test the demand for its idea. Nick Swinurm used the drop shipping approach for Zappos, a classic example of the concierge MVP.
Nick was a software engineer who couldn’t afford to invest in a large inventory of shoes, so he posted pictures of shoes from local stores on his WordPress website.
If a customer purchases based on the listed product, he purchases it and ships it to users. This allows him to validate the demand for his idea without incurring the expense and risk of maintaining a large inventory.
The concierge approach is about doing things manually and keeping the MVP cost minimal without relying on automation or coding.
However, you need to ensure the beta tester gets every detail correct. For example, if you are a startup claiming to automate software development, there should be no manual coding.
So, if you are building MVP, ensure you keep minimal automation and quickly provide an essential product version.
You need to understand that the concierge approach suits the eCommerce products best compared to other domains.
3) AngelList
The initial concept for AngelList’s MVP was to improve the existing startup ecosystem. It was designed as a platform to help entrepreneurs with fundraising.
Initially, the platform had only essential features like registration, investor search, and connecting with investors.
This was the MVP development approach, which followed the lean startup model. The Lean Startup model allowed the AngelList team to launch a platform quickly with minimal cost.
AngelList expanded and added new features to delight its users as the platform proved valuable to startups.
For example, it now includes a platform for recruiting employees and a secondary market where investors can buy and sell shares in private companies.
The 4 Types of Minimum Viable Products
MVP types can be many based on what is your business objective. For example, if you want to test your product with minimal coding, you can leverage the no-code approach.
1. Landing Page/Fake Door MVP
The Landing Page MVP is an approach in which a specific website is designed to build an audience and collect user feedback. It acts as a platform to test the viability of your product idea through user feedback.
You can validate and even pre-sell the product concept using the fake door MVP development.
Monitoring interactions such as scrolling patterns, click-through rates, and time spent on specific pages will help you identify which features resonate with your customers.
Benefits of Fake Door MVP
2. No-Product MVP
The No-Product or No-Code MVP is another way of MVP development that focuses on product validation.
This method includes marketing the product and gaining customer insights without putting effort into coding.
Benefits of No-Product MVP
3. Single-Feature MVP
It is a type of MVP that emphasizes developing just one essential feature of your app, making it a high-fidelity approach. You must identify the core functionality crucial to your app’s value proposition.
Take an example of a navigation app that allows users to search nearby locations on the maps.
Initially, you can focus on MVP development, considering the essential feature of location search based on proximity.
Further, based on customer feedback, you can add other features like route planning and navigation capabilities.
Benefits of Single-Feature MVP
4. Wizard-Of-Oz MVP
This type of MVP offers the user the illusion of a full-fledged product. While it seems like your product is fully functional, actual operations occur in the background.
This approach is best if you plan to introduce new technologies and innovations to your audience.
For example, if you are developing a generative AI app, you can focus on this type of MVP building.
Provide essential query support for generative AI tools and further iterate to create more advanced functions.
Benefits of Wizard-Of-Oz MVP
Your needs will determine the right MVP-building approach for your business. Consider a lightweight cloud-based option if you are developing an MVP for a SaaS product.
However, it can differ based on your organizational goals, audience, and the type of SaaS product features you prioritize.
Once you decide on the type of MVP you want to build, it’s time to understand the crucial steps.
How to Build a Minimum Viable Product
Strategic development and testing can impact your outcomes if you plan to build MVP for your SaaS product.
For example, if you plan to develop a landing page MVP, strategic content and testing it for security is crucial. So, to ensure optimal MVP development, you can follow the below steps,
Step 1: Start with Market Research
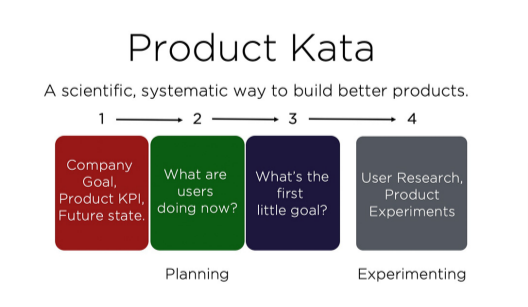
These steps, which you will discover in this article, focus on a specific framework called “Product Kata.” Toyota introduced it in its manufacturing process.
You can leverage this framework to build better products.
According to this framework, there are four essential aspects of MVP development divided into planning and experimentation phases,
The first step is to define your goals, KPIs, and future objectives. This means you must research the market to define MVP development’s goals.
Plus, it would be best if you determined the KPIs to measure and evaluate MVP testing results. Lastly, you also need to finalize the state of your product after MVP building and testing.
Step 2: Ideate on Value Addition
This is where you ideate product features and attributes to add value. Understand the user’s perspective and identify their pain points. Next, compare the existing product with your solution and try to add more value.
It would be best to research what customers are doing to solve the problem and what difference your product will make.
Step 3: Map Out User Flow
Once you have figured out the features and attributes that can add value and define smaller goals, these goals will act as critical junctions along the MVP development process.
The best way to determine key junctions in MVP development is to map out a user flow.
This means understanding the critical interaction points along the user journey and adding them to your list of goals.
For example, if your login page is the first interaction point, your first goal will be to minimize the time needed to log on to the app or website.
Step 4: Prioritize MVP Features
Prioritizing the MVP features includes deciding which ones to focus on when conducting user research.
You can plan the user research based on two main categories of features. One category includes all the core features of your product. In contrast, others are primarily non-essential features.
Match these feature categories with the user flow you decided on in the third step, and then conduct thorough user research. Your research will be based on customers’ experiences with the MVP.
Step 5: Launch MVP
Launch the type of MVP you have finalized with prioritized features. Conduct thorough user research and gather feedback. You need to have a feedback integration process streamlined to ensure continuous improvements.
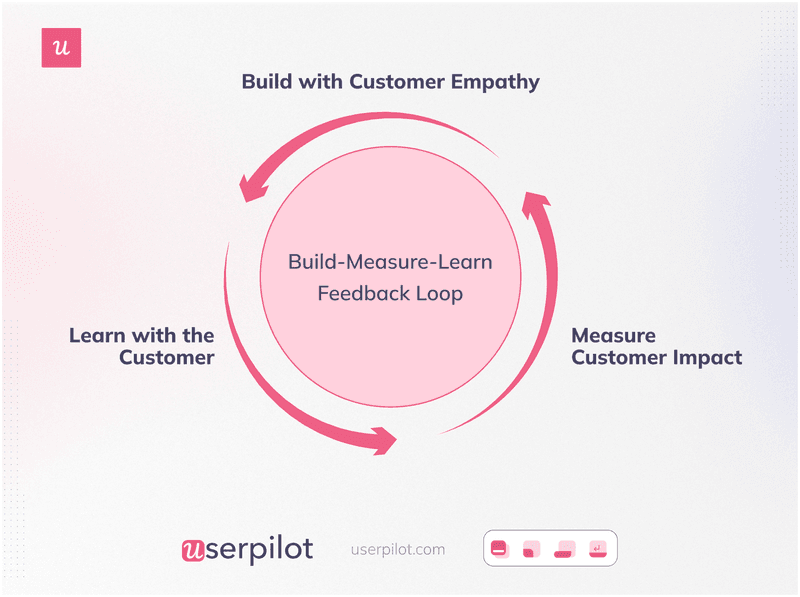
Step 6: Exercise ‘B.M.L.' — Build, Measure, Learn
This is the last and most crucial stage of MVP development. You have had the MVP soft launched; now is the time to experiment.
Most MVP implementation revolves around three significant stages: Build, Measure, and Learn.
This includes building your MVP based on prioritized features and measuring the KPIs defined in the first stage.
Repeat the cycle of build, measure, and learn for optimal results. Going in-depth into this BML approach are the following steps,
Step 1) Develop a User Base
Developing a user base for your BML requires a marketing campaign that excites audiences. You can run a website-based campaign like Zeppos or promote the MVP on social media platforms.
The primary purpose of this exercise is to increase user participation. A modern approach is crowdfunding, which allows you to ask users to join your MVP trials.
Step 2) Collect Usage Data
Collecting usage data from your user base can take different forms. For example, you can ask them to use the MVP physically or virtually. You can opt for virtual usage data if your user base is larger.
This can include simulations, websites, web apps, or other digital versions. When dealing with such a large amount of information, you will also need data management systems and infrastructure.
The best practice for efficient MVP building and data management is to hire professionals.
Step 3) Ask for user feedback
User feedback is the next critical stage and is the measuring part of BML. It allows you to analyze user behavior and how they interact with your product.
You can map their feedback with different interaction points across the user flow and optimize the customer journey.
Step 4) Update Your SaaS Product
Your SaaS product optimization will begin once you receive feedback from users.
Analyze the product’s usage and determine changes impacting the user experience. Identify unique usage patterns to ensure you know which changes to prioritize.
The BML approach will give you insights into your target audience, their SaaS product usage, and footnotes on what changes to make.
However, it can be a miss if you don’t have the right audience for MVP usage analysis.
The Road to Hell is Paved with Perseverance
Perseverance is no doubt a tough nut to crack, but it still has the perk of getting your SaaS product successful.
Pivoting and perseverance need to go hand-in-hand for success. Giants like Slack, Flickr, and Groupon have proved this from time to time.
Here are some pivot examples and types you can leverage for your SaaS products.
1. Zoom-In Pivot
This is a pivot in which you focus on a feature that becomes the center of attraction for your audience. The most exciting part—“You Never Expected It!” Take an example of Slack or Flickr.
Both were internal tools for developers and gamers. However, they pivoted when these SaaS companies saw potential in otherwise unexpected features.
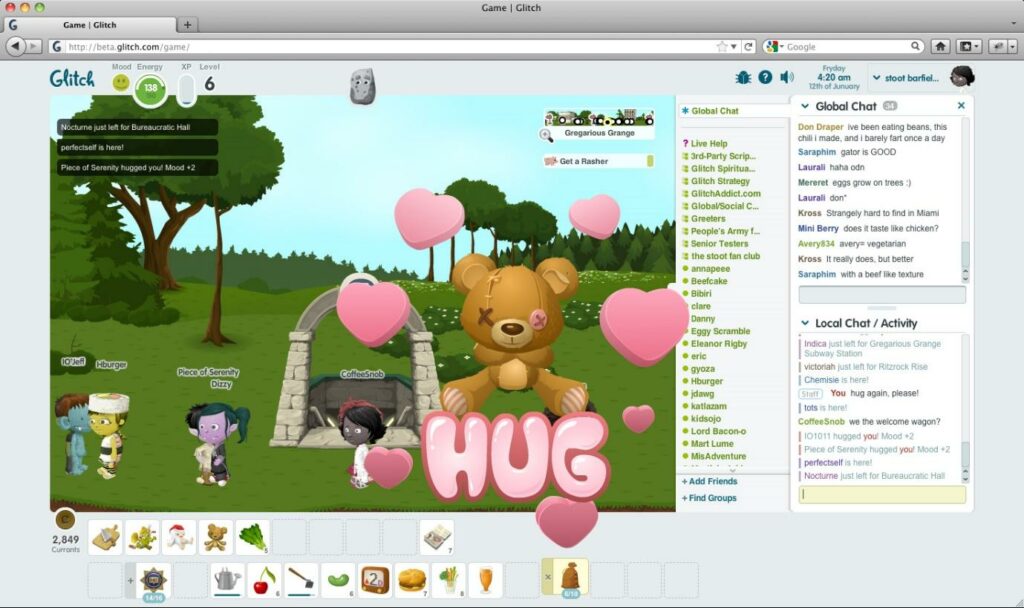
Slack was originally “Glitch.” Tiny Speck was the company behind Glitch, a game destined for doom. Yes, the game did not work, and Tiny Speck pivoted to a messaging tool for workplaces today known as Slack.
Fun Fact: Slack was an internal tool developed by engineers at Tiny Speck to communicate within the organization.
With this pivot approach, you need to zoom in and find that one feature you can leverage for success.
2. Zoom-Out Pivot
This is a pivot approach opposite to the zoom-in pivot! This means you need to add extra functionality to your SaaS product.
What functionalities you need to add can be determined through MVP development and feedback integrations.
3. Customer Segment Pivot
SaaS enterprises and startups often have side projects with entirely different customers. Sometimes, these side projects take the shape of full-fledged success stories due to a specific customer segment.
Groupon is a classic example of a customer segment pivot. Started in a fundraising capacity known as “The Point,” Groupon was launched as a side project.
However, this venture became more successful than the original fundraising campaign, attracting a specific segment of customers.
4. Customer Needs Pivot
There are days when SaaS companies get it right, and there are days when they don’t. And when they don’t get it right, pivot saves the day.
Yes, many companies have tried to solve user problems over the years but failed to do so in one way. However, they succeeded when they pivoted.
Netflix is a classic example of this pivot. Netflix was competing against Blockbuster, which was in the DVD rental business.
IT was successful, but an actual market difference was their streaming service. It pivoted from renting DVDs to providing content streaming and is now a market leader.
5. Platform Pivot
The SaaS business model is amazing, and companies often build platforms for seamless performance.
However, sometimes, the platform outgrows software for SaaS businesses. This pivot from a SaaS to a PaaS company can be game-changing.
6. Business Architecture Pivot
This is similar to platform pivot, but here, you are not just pivoting to a platform-based model, but you restructure the entire business.
For example, you may pivot from B2B to B2C and vice versa. Similarly, you may rotate from a free SaaS product to a freemium or premium model with the value capture pivot.
7. Value Capture Pivot
It is a type of pivot that allows SaaS businesses to improve revenues through pivoting from one model to another.
As your business grows, you can discover new avenues of value capture and pivot the revenue models accordingly.
8. Engine of Growth Pivot
Engines of growth are your sources that help businesses grow. For example, if your business is popular among customers and they refer it to others, such an engine of growth is called “viral.”
Similarly, it’s a sticky growth engine if your brand managers retain customers and slow churn rates.
Lastly, you have a paid growth engine if your customer acquisition cost is low and customer lifetime value is higher.
Pivoting between these engines of growth can help your business overcome the challenges of a competitive market.
9. Channel Pivot
The channel you choose to provide the SaaS product is what you can pivot for better sales and conversions.
For example, you can look to list your product on a SaaS marketplace rather than going through conventional sales channels.
10. Technology Pivot
Many SaaS companies often look to offer solutions using specific challenges. However, these technologies have become obsolete over time and need to be more efficient.
This is where businesses can pivot from one technology to another for better SaaS delivery.